Venture capital (VC) is a type of private equity financing that is typically provided to early-stage companies with high growth potential.
VC firms invest in these companies in exchange for equity ownership, with the expectation of receiving a return on their investment when the company goes public or is acquired by another company.
While venture capital has been around for several decades, it has gained popularity in recent years as more entrepreneurs seek funding to grow their businesses.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of venture capital, including its history, the players involved, the fundraising process, and the risks and rewards of investing in early-stage companies.
A Brief History of Venture Capital

Venture capital had its roots in the United States in the 1940s and 1950s, when a group of wealthy individuals began investing in new and innovative businesses. These early venture capitalists, known as “angel investors,” provided funding to companies in exchange for equity ownership.
However, it wasn’t until the 1960s and 1970s that venture capital became a formal industry, with the establishment of firms such as Kleiner Perkins and Sequoia Capital.
During the 1980s and 1990s, venture capital experienced a period of rapid growth, fueled in part by the tech boom. Many VC firms focused on investing in technology startups, which had the potential for explosive growth and high returns. However, the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s and early 2000s led to a downturn in the industry, as many of these companies failed to live up to their hype.
Since then, the venture capital industry has rebounded, and today it is a major player in the global economy. In 2020, venture capital firms invested a record $300 billion in startups worldwide, according to data from PitchBook. This represents a significant increase from the $77 billion invested in 2010.

Looking to start investing, why not try Tiger Broker?
Tiger Brokers offers competitive commission fees for trades across different markets.
It is also practically fee-less in these aspects: no custody fees, deposit (or withdrawal) fees, currency exchange fees, inactivity fees, or account maintenance fees to contend with!
The Players Involved in Venture Capital
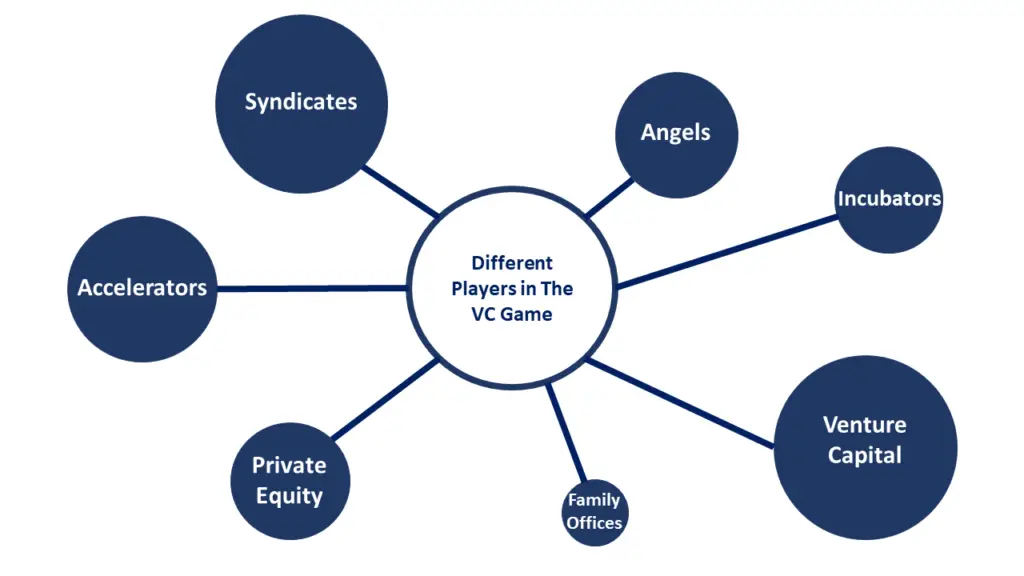
Venture capital is a complex industry that involves many different players. Here are some of the key players involved in venture capital:
Venture Capital Firms: These are the firms that provide funding to early-stage companies. VC firms raise money from institutional investors such as pension funds, endowments, and wealthy individuals, and then use this money to invest in startups.
Limited Partners (LPs): These are the institutional investors who provide the capital to VC firms. LPs include pension funds, endowments, foundations, and family offices.
General Partners (GPs): These are the individuals who manage the VC firm and make the investment decisions. GPs are typically experienced investors who have a track record of success in the industry.
Startups: These are the companies that receive funding from VC firms. Startups are typically early-stage companies that have high growth potential.
Entrepreneurs: These are the individuals who start and run the startups. Entrepreneurs are responsible for developing the product or service, building the team, and growing the business.
Advisors: These are the individuals who provide guidance and advice to the startups. Advisors may be experts in a particular industry or have experience scaling a startup.
The Fundraising Process
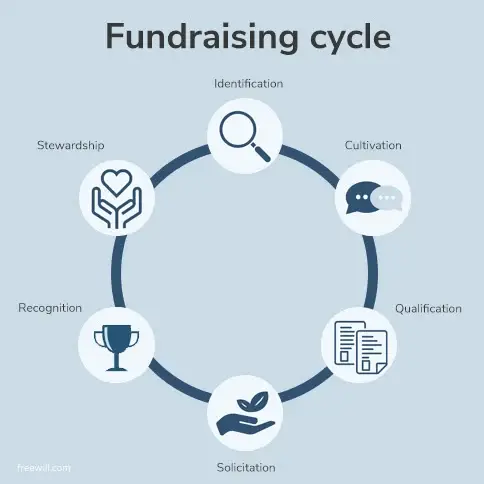
The fundraising process for venture capital can be lengthy and complex. Here are 6 key steps involved in raising funding from a VC firm:
Identify potential investors: The first step in raising funding from a VC firm is to identify potential investors. This typically involves researching VC firms that have a history of investing in companies in your industry or stage of development.
Pitch your business: Once you have identified potential investors, the next step is to pitch your business to them. This typically involves creating a pitch deck that outlines your business model, market opportunity, and financial projections.
Due diligence: If a VC firm is interested in investing in your company, they will conduct due diligence to verify your claims and assess the risks and potential returns of the investment. This may involve reviewing financial statements, conducting market research, and speaking with customers and industry experts.
Term sheet: If the VC firm decides to move forward with the investment, they will provide a term sheet that outlines the terms of the investment, including the amount of funding, the valuation of the company, and any other conditions or restrictions.
Negotiation: Once the term sheet is issued, negotiations will begin between the startup and the VC firm to finalize the terms of the investment. This may involve back-and-forth discussions over the valuation, the amount of equity the VC firm will receive, and other terms.
Closing: Once the negotiations are complete and the terms are agreed upon, the deal will be closed, and the funding will be provided to the startup. This typically involves signing legal documents and transferring funds.
The Risks and Rewards of Investing in Early-Stage Companies
Investing in early-stage companies can be risky, as many startups fail to achieve their goals or generate significant returns for their investors. Across almost all industries, the average failure rate for year one is 10% However, in years two through five, a staggering 70% of new businesses will fail.
However, there are also significant potential rewards for those who are successful. Here are some of the risks and rewards of investing in early-stage companies:
Risks:
High failure rate: The majority of startups fail, and even successful startups can take years to generate returns for their investors.
Illiquidity: Investments in early-stage companies are often illiquid, meaning it may be difficult to sell your shares or receive a return on your investment until the company goes public or is acquired.
Lack of control: As a minority shareholder, you will have limited control over the company’s operations and decision-making.
Rewards:
High potential returns: Successful startups can generate significant returns for their investors, with some companies achieving returns of 10x or more.
Diversification: Investing in a portfolio of startups can provide diversification and potentially reduce overall risk.
Access to new technologies and markets: Investing in early-stage companies can provide access to new technologies and markets, which may not be available through traditional investments.
Conclusion
Venture capital is a key driver of innovation and economic growth, providing funding and support to early-stage companies with high growth potential. While the industry has its risks, it also has significant potential rewards for those who are successful. As an entrepreneur or investor, it’s important to understand the ins and outs of venture capital and to work with experienced professionals who can guide you through the fundraising process and help you navigate the risks and rewards of investing in early-stage companies.





