A put option in stocks is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific amount of an underlying security at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
Understanding what is a put in stocks, how puts work and their strategic applications is essential for investors looking to manage risk and potentially profit in a bearish market. Let’s explore the key concepts related to puts in stocks:
Key Takeaways
- Buying Put Options (Long Puts) allows traders to implement a bearish strategy with less risk than short-selling and take advantage of leverage.
- Put options provide the right to sell at a predetermined price, are profitable when the stock falls below the strike price, and do not require the holder to sell.
- Protective Puts act as a downside protection strategy, serving as an insurance policy against losses and are preferred by traders seeking protection for their positions.
How Put Options Work

Right to Sell at Predetermined Price
A put option embodies the right to sell a particular stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. This right is a cornerstone of put options, providing the holder with the power to sell shares at a favorable price, regardless of the market’s current conditions. If the market price of the stock falls below the strike price, the option holder can still sell at the higher strike price, effectively setting a floor for potential losses.
The beauty of put options lies in the flexibility they offer. Holders can decide not to exercise the option if the market price is more advantageous, thus the option can expire worthless, limiting the holder’s loss to the premium paid.
For example, consider a scenario where a stock is currently trading at $100, and an investor purchases a put option with a strike price of $90 for a premium. If the stock price drops to $80, the investor can exercise the option and sell the stock for $90, realizing a gain despite the market downturn.
Profitable when Stock Falls Below Strike Price
When an investor purchases a put option, they gain the potential to profit when the stock’s market price falls below the strike price. The further the stock price drops below the strike price, the greater the profit for the put option holder, assuming the option is exercised before expiration.
- Stock Price Above Strike Price: The put option is out of the money, and the investor may face a loss limited to the premium paid.
- Stock Price Equal to Strike Price: The option is at the money, and the investor’s loss is typically the premium paid.
- Stock Price Below Strike Price: The put option is in the money, and the investor can profit from the difference between the stock price and the strike price, minus the premium paid.
The beauty of put options lies in their ability to provide significant profits from a declining stock with a relatively small investment. This asymmetry between risk and potential reward is a core appeal of options trading.
It’s essential to understand that while put options can be lucrative, they are not a guarantee of profit. Market conditions, such as a fall in implied volatility, can affect the outcome of the trade. Additionally, the timing of the market movement is crucial; a sharp move lower early in the trade can be detrimental.
No Obligation to Sell
One of the most appealing aspects of put options is the flexibility they offer. Investors have the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying stock at the strike price before the expiration date. This means that if the market price is unfavorable, the investor can simply let the option expire, losing only the premium paid for the put option.
Flexibility is a key advantage of put options. Consider the following scenarios where this flexibility can be beneficial:
- The stock price remains stable, and the put option expires worthless, resulting in a loss limited to the premium.
- The stock price increases, making the put option less valuable, but the investor is not required to sell and can hold onto the stock for potential future gains.
- The stock price decreases, and the investor can exercise the option to sell at the strike price, potentially mitigating losses.
By not being obligated to sell, investors can avoid additional losses that might occur from selling the stock in a declining market. This protective feature is what distinguishes put options from short selling, where the obligation to buy back the stock can lead to unlimited losses.

Looking to start investing, why not try Tiger Broker?
Tiger Brokers offers competitive commission fees for trades across different markets.
It is also practically fee-less in these aspects: no custody fees, deposit (or withdrawal) fees, currency exchange fees, inactivity fees, or account maintenance fees to contend with!
What Is A Put In Stocks – Protective Puts
Downside Protection Strategy
A protective put strategy is akin to an insurance policy for stock investors, offering a safeguard against declining stock prices while maintaining the potential for profit. By purchasing a put option, investors can set a floor on potential losses, ensuring that their investment won’t fall below a certain value, even if the market takes a downturn.
italics[Downside protection](https://www.supermoney.com/encyclopedia/downside-protection)italics is a critical aspect of this strategy, as it allows investors to hedge against short-term market volatility without sacrificing long-term bullish positions. For example, if an investor is optimistic about a stock in the long run but concerned about possible short-term setbacks, a protective put provides a buffer against those temporary dips.
The beauty of protective puts lies in their flexibility; they can be tailored to match the investor’s risk tolerance and investment horizon.
Here are some considerations when implementing a protective put strategy:
- Assess the level of protection needed based on the investment’s risk profile.
- Determine the appropriate strike price and expiration date for the put option.
- Calculate the cost of the put and weigh it against the potential benefits of downside protection.
While protective puts offer a measure of security, investors should be aware that the cost of the option premium could offset potential gains. It’s essential to understand the trade-offs involved and to have a risk management plan in place.
Insurance Policy Against Losses
Much like various forms of insurance provide a safety net for unforeseen events, protective puts offer investors a mechanism to shield their portfolios from potential downturns. By purchasing a protective put, investors effectively secure an insurance policy for their stocks, ensuring that they can mitigate losses should the market take an unfavorable turn.
While no one wishes for a market decline, protective puts grant peace of mind, allowing investors to maintain their positions with less fear of significant loss.
The concept is straightforward: when you buy a protective put, you pay a premium, similar to an insurance premium, for the right to sell your shares at a predetermined price. This strategy is particularly preferred by traders who seek protection without the need to liquidate their holdings.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how protective puts compare to other insurance types:
- Cyber insurance: Protects against cyber-attacks.
- General insurance: Covers a range of unforeseen events.
- Motor, travel, home, and maid insurance: Offers specific coverage.
- Wealth accumulation insurance: Combines protection with investment opportunities.
- Protective puts: Serves as a safety net against potential losses in the stock market.
Preferred for Traders Wanting Protection
Traders who own the underlying asset and seek to safeguard their investments against potential downturns often turn to protective puts. This strategy serves as an insurance policy, providing peace of mind by capping potential losses while allowing for continued participation in any upside potential.
For instance, consider a trader with a bullish outlook on a stock but who wishes to hedge against short-term volatility. By purchasing a protective put, the trader ensures that they can sell their shares at a predetermined price, even if the market price plummets. This approach is particularly appealing for those with a significant investment in a single stock or portfolio.
The cost of protection is a key consideration; it varies depending on the level of coverage desired. A higher level of protection typically comes with a higher premium.
Margin requirements for a protective put are also an important factor. When a long put is paired with a round-lot of long shares, it constitutes a protective put, which may affect the margin needed for the trade.
In summary, protective puts are a strategic choice for investors who prioritize security over potential gains. They are a testament to the adage that sometimes, the best offense is a good defense.
Understanding the importance of risk management in your investment portfolio is crucial, and one effective strategy is the use of protective puts. This method allows you to safeguard your stock investments against potential downturns, ensuring peace of mind and financial security. To learn more about how protective puts can fortify your investment strategy, visit our comprehensive guide on [HustleVentureSG](https://www.hustleventuresg.com). Don’t leave your investments to chance; arm yourself with knowledge and take control of your financial future today!
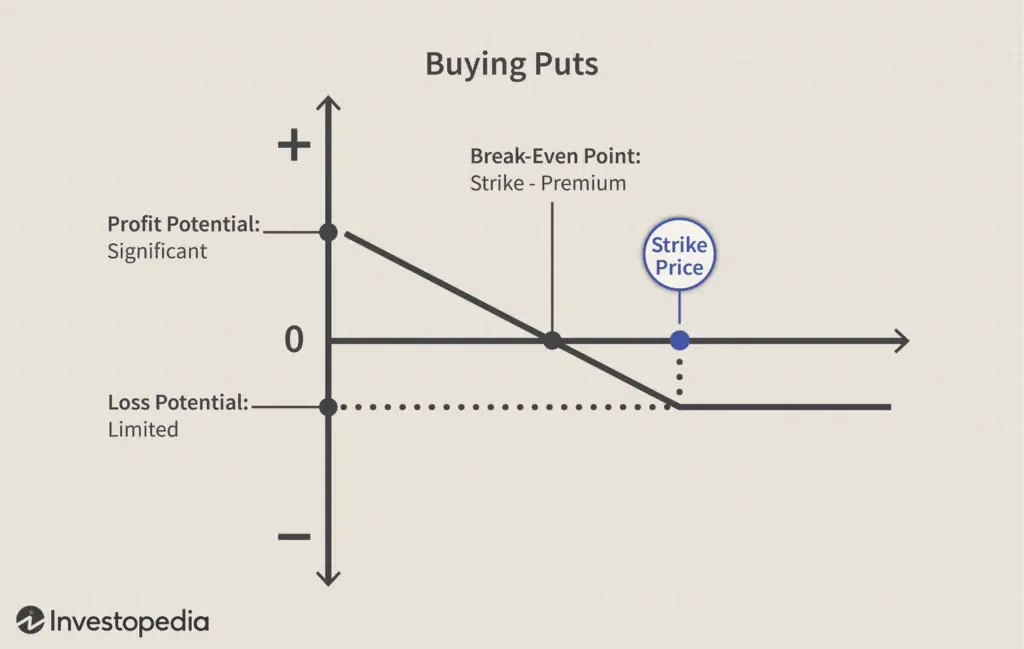
Buying Put Options (Long Puts)

Bearish Strategy
In the realm of options trading, a bearish strategy involves anticipating a decline in the price of a stock. One common approach is the bear put spread, which is designed to profit from a downward price movement. This strategy entails buying a put option at a specific strike price while simultaneously selling another put with a lower strike price.
The bear put spread is particularly appealing during market downturns or when uncertainty looms over the financial markets.
Here are some key characteristics of a bearish strategy using put options:
- Directional bias towards a declining market
- Potential to profit from falling stock prices
- Utilization of spreads to manage risk
Bearish strategies are not just limited to bear put spreads; there are multiple options to consider, such as the Bear Call Spread, Strip, Synthetic Put, and Bear Butterfly Spread. Each strategy has its nuances and is selected based on the trader’s market outlook and risk tolerance.
Less Risk than Short-Selling
When comparing put options to the traditional method of short-selling, one of the most significant advantages is the reduced risk profile. Buying a put option limits the investor’s loss to the premium paid for the option, unlike short-selling, where losses can be theoretically unlimited. Short sellers are essentially wagering that a stock will drop in price, but if the stock price rises, the potential losses can exceed the initial investment.
In contrast, put options provide a more controlled way to bet on a stock’s decline. The table below illustrates the difference in potential losses:
| Strategy | Maximum Loss |
|---|---|
| Short-Selling | Unlimited |
| Buying Put Options | Premium Paid |
By opting for put options, investors can define their maximum possible loss upfront, which is particularly appealing for those cautious about the unpredictable nature of the stock market.
Furthermore, when closing a short position, a trader must repurchase the shares at the current market price, which could be significantly higher than the price at which they borrowed the asset. This process can lead to substantial losses if the market moves against the trader. Put options, on the other hand, come with no obligation to sell, offering a more flexible and less risky alternative.
Leverage Advantage
The concept of leverage is a powerful tool in the world of investing, particularly when it comes to options trading. Buying put options allows investors to control a larger amount of stock with a smaller initial investment, which can lead to amplified returns if the market moves in their favor. This is because the cost of a put option is typically much less than the cost of the underlying stock itself.
For instance, consider an investor looking to bet against a stock priced at $100 per share. Instead of shorting 100 shares for $10,000, the investor could purchase put options with a fraction of that amount. If the stock price declines as expected, the investor could realize significant gains relative to their initial outlay.
While leverage can magnify profits, it’s important to remember that it can also increase potential losses. The premium paid for the option is the maximum risk the investor faces, but this cost can add up if multiple options are purchased.
Options trading, with its leverage capabilities, offers a strategic advantage for those looking to capitalize on market movements without committing large sums of money upfront.
Conclusion
In conclusion, put options in stocks provide investors with the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a predetermined price before its expiration date. This strategy is commonly used by traders who are bearish on a particular stock and want to take advantage of falling prices with less risk. Additionally, investors can also sell put options, known as a “short put” position, to potentially acquire shares at a lower price. Understanding put options is essential for managing risk and maximizing returns in the stock market.

Looking to start investing, why not try Tiger Broker?
Tiger Brokers offers competitive commission fees for trades across different markets.
It is also practically fee-less in these aspects: no custody fees, deposit (or withdrawal) fees, currency exchange fees, inactivity fees, or account maintenance fees to contend with!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a put option in stocks?
A put option in stocks gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price before the expiration date.
How is buying put options different from short-selling?
Buying put options is a bearish strategy that involves less risk than short-selling, allowing traders to take advantage of falling prices with leverage.
When is a put option profitable?
A put option is profitable when the stock falls below the strike price, minus the cost of the option.
What is the difference between a long put and a short put?
A long put gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset, while a short put obligates the seller to buy the asset at a certain price.
Why would someone use a protective put strategy?
A protective put provides downside protection by acting as an insurance policy against potential losses in the underlying asset.
Can investors sell put options as well?
Yes, investors can sell put options to generate income or potentially acquire shares at a lower price if the option is exercised.